Best in Manufacturing – February 11, 2018
Each Sunday, we publish a list of top articles and other content related to manufacturing in areas like quality control, product development, supply chain management, sourcing, auditing and law.
1. The effect of autonomous vehicles on manufacturing
What exactly is industrial mobility? In short, it’s how we move goods and commodities in industrial settings or for industrial purposes.
This featured article examines how industrial mobility will affect manufacturing. The article references a research report recently released by PricewaterhouseCoopers, entitled Industrial Mobility: How Autonomous Vehicles Can Change Manufacturing.
The report mentions how autonomous vehicles aren’t just cars, boats, trains and so on, that you would find outside. It also includes autonomous, mobile robots on factory floors.
Most manufacturers, as the report indicates, haven’t seized the opportunity that is autonomous mobility in their operations. From the featured article:
Only about 9% of manufacturers say they have adopted some kind of semi-autonomous or autonomous mobility within their operations, with another 11% saying they expect to do so in the next three years.
These aren’t sky-high numbers. Yet the article points out how, with a definition of 30 percent adoption considered as being mainstream, then industrial mobility technologies are en route to that target.
Most of the surveyed manufacturers are awaiting the arrival of autonomous trucks, like the Tesla Semi (among others). These autonomous vehicles are viewed as having great potential, and for good reason. The report indicates that 90 percent of manufacturers surveyed feel autonomous trucks could save up to 25 percent of total trucking costs.
Although autonomous trucks tend to take the spotlight, as the report cited by this featured article makes clear, there are even more potential benefits for manufacturing stemming from autonomous industrial mobility.
If you’d like to read this featured article to learn more about industrial mobility, follow the link below:
PwC: How Autonomous Vehicles Are Changing Manufacturing – John Paul Hampstead, Freight Waves
2. How industrial robots are affecting manufacturing [VIDEO]
This year, there will be roughly 2.3 million industrial robots operating across the planet. These robots have already and will continue to replace some human workers. While this may seem like a downside, the robots will also contribute to greater productivity and lower costs.
The 2.3 million robots are just the beginning. Mankind is not quite at the point of full automation, but we’re certainly taking steps toward it.
This featured video examines some of that progress and focuses on Asia in particular. The video looks at companies already using robots in places like Japan and Shenzhen, and even interviews some of the masterminds designing robots. The video points out Chinese demand for robots grew by 20 percent last year alone, mostly due to rising labor costs and an aging workforce.
Interestingly, the video points out that despite robots replacing certain jobs, the future holds opportunities for those displaced by automation in the service sector. After all, only humans can do some jobs. In fact, the category of jobs that is growing the fastest in China now is in the services sector, not manufacturing.
If you’re curious about the future of robots in manufacturing, you can watch the full video in the link below:
The Robot Revolution: The New Age of Manufacturing - Moving Upstream – Jason Bellini, The Wall Street Journal
3. A list of considerations for your China manufacturing agreement
It’s Friday night and you just finished the tour of your prospective factory in China. You go out to dinner with the factory’s management and have a wonderful meal, full of laughing and 干杯s (gānbēi, literally “dry glass”, aka cheers in Chinese).
 Then the time comes to talk business. You and the factory staff are both inebriated, but the discussion is a challenge of wits and business fortitude that you feel prepared for. After an intense 45 minutes, you feel like you’ve reached a good deal. Your counterparts seem pleased as well.
Then the time comes to talk business. You and the factory staff are both inebriated, but the discussion is a challenge of wits and business fortitude that you feel prepared for. After an intense 45 minutes, you feel like you’ve reached a good deal. Your counterparts seem pleased as well.
Unfortunately, the great deal you think you’ve sealed is nothing more than hot air until it manifests as a mutually-agreed upon manufacturing contract. And even if you do sign a manufacturing agreement, you may have forgotten to discuss certain provisions at that fateful, 干杯 ridden dinner, which means they won’t be in the contract.
Thankfully, China Law Blog offers some points that you need to consider for your manufacturing contracts. As this featured article points out, what you need to include in your own contract might vary. But the considerations offered are a great way to get you thinking about what else you need to discuss with your supplier and incorporate in a manufacturing agreement.
Some screenshots from this featured article are below: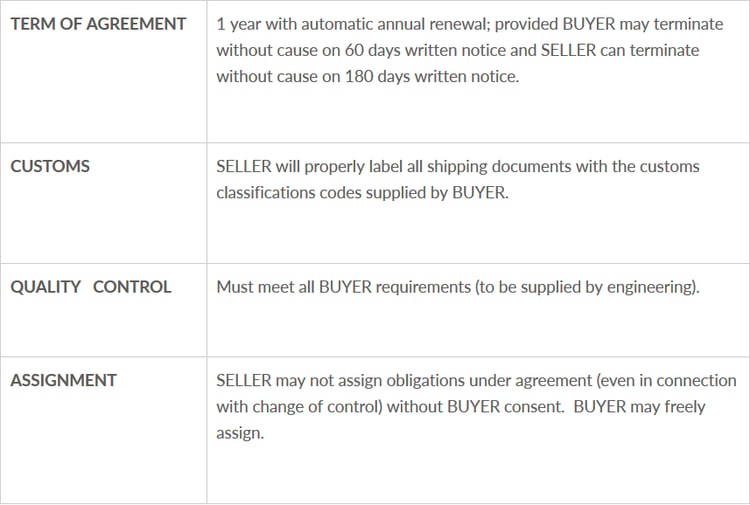
What’s above is just a taste of the insight offered in this featured article. To improve your manufacturing agreements and protect your business, check out the featured article in the link below:
Quick Question Friday: China Law Answers, Part XLVII – Dan Harris, China Law Blog
4. Blockchain in supply chains
Blockchain is a technology poised to change the world. In case you’re not familiar with how it works, you can find an explanation here.
Most people nowadays know of blockchain because of its role in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. But blockchain technology has applications beyond virtual currency.
This featured article mentions a specific application of blockchain to logistics. Named “Provenance”, this project aims to bring transparency to supply chains and encourage companies to source products ethically.
Using applications like Provenance, customers and companies are able to track interactions in a supply chain because of the “digital handshake” at every stage. For example, when your product is sent from a supplier to a warehouse and checked in, that will be unalterably recorded in the blockchain. No one can change the receipt timestamp without everyone else in the blockchain knowing.
For end consumers, customers can utilize the data blockchain tracks to make more informed purchasing decisions. When it comes to companies and how they benefit, they’ll gain the ability to more accurately track goods and identify weak points in their supply chains.
While this system of digital handshakes and verification might not seem very groundbreaking, blockchain technology is still evolving, and it truly does hold great potential. Businesses and consumers will continue to discover new use cases and develop new ways to utilize blockchain to meet the demands of the market.
Imagine you’re a major firm that has supply chains scattered across the globe. Aided by blockchain, you’ll have greater insight into the scores of networks and individual interactions that ultimately create your products. This knowledge will be invaluable and will lead to more intelligent business decisions.
Even though blockchain in supply chains is still in its infancy, it’s important to learn about this tool and how it will one day enhance operations. To learn more about blockchain in supply chains, check out the featured article in the link below:
Supply Chains Are Messy. Blockchain in Supply Chain Can Help – Adam Robinson, Cerasis
5. Intel’s new augmented reality smart glasses
Augmented reality glasses hold great potential for improving manufacturing operations.
 For instance, instead of workers having to look back and forth between a computer screen or instruction manual and the part they’re inspecting or assembling, they can instead don a device to provide real-time guidance.
For instance, instead of workers having to look back and forth between a computer screen or instruction manual and the part they’re inspecting or assembling, they can instead don a device to provide real-time guidance.
Some notable names in this space are Google Glass and the Microsoft Hololens. And now, Intel is joining the battle for providing augmented reality glasses.
Intel’s New Devices Group is currently designing their “Vaunt Glasses”. The device works by shining a special low-powered laser onto your retina, called a “vixel”. Vixel stands for “vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser”. Intel says the device is safe and that the laser is “at the very bottom end of a class 1 laser”.
The Vaunt Glasses aren’t being designed specifically for manufacturing. In fact, they’re meant to only provide basic information to users with a heads-up display. Despite not providing as much information as, say, Google Glass or the Microsoft Hololens, Vaunt has yet to be released. Testers and early adopters haven’t had the chance yet to discover use cases for manufacturing.
There’s also the chance that some manufacturers and designers don’t really need heaps of complex information in their augmented reality devices. For some users, minimal might be best. They might prefer Vaunt because it only gives them the basics and doesn’t overwhelm and distract them with torrents of data.
You can watch the full video covering Intel’s smart glasses below:
Exclusive: Intel's New Smart Glasses Hands-on – The Verge via YouTube
We’re constantly scanning the web for top manufacturing stories and news. If you’d like to submit an article for consideration for our weekly Best in Manufacturing, send us a message and let us know.







